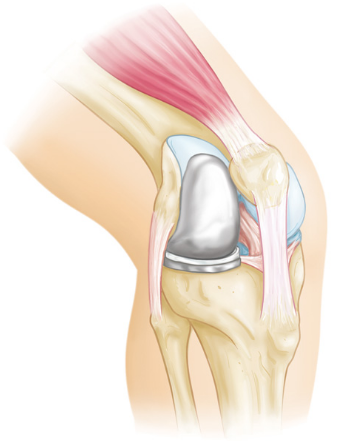
 Partial knee replacements are designed to replace only the abnormal part of the knee joint instead of the entire joint. These are suitable where the degenerative changes are localised to one compartment of the knee.
Partial knee replacements are designed to replace only the abnormal part of the knee joint instead of the entire joint. These are suitable where the degenerative changes are localised to one compartment of the knee.
The knee joint is a complex joint formed between the lower end of thigh bone (femur) and the top end of the leg bone (tibia). The lower end of femur is like an hourglass in cross section forming two rounded condyles. These articulate with the tibia to form the medial (inner) and the lateral (outer) compartment of the knee.
In addition, the knee cap (patella) articulates with the lower of femur to form the patellofemoral joint. This makes a total of three parts in the knee joint –
1. Medial tibio femoral joint (Inner part of the knee)
Replacement of the Medial Compartment of the knee
Note the loss of space (arrow) between the two bones on the X ray on the left. The X ray on the right shows replacements of part of femur and tibia. The space between the metal parts (dense white) is the plastic which forms the bearing surface of the knee. This is an example of the Oxford design
-
 Arthritis of medial compartment of the knee
Arthritis of medial compartment of the knee
Arthritis of medial compartment of the knee
Arthritis of medial compartment of the knee
-
 Medial compartment replacement
Medial compartment replacement
Medial compartment replacement
Medial compartment replacement
https://cardiffhipandknee.com/knee/partial-knee-replacements#sigProId1aed5195a2
2. Lateral tibio femoral joint (Outer part of the knee)
Replacement of the Lateral Compartment of the knee
Note the loss of space (arrow) between the two bones on the X ray on the left.This is on the outer side of the knee. The X ray on the right shows replacements of part of femur and tibia. The space between the metal parts (dense white) is the plastic which forms the bearing surface of the knee.
Replacements of the lateral part of the knee are relatively rare.
-
 Lateral compartment arthritis of the knee
Lateral compartment arthritis of the knee
Lateral compartment arthritis of the knee
Lateral compartment arthritis of the knee
-
 Lateral compartment replacement of the knee
Lateral compartment replacement of the knee
Lateral compartment replacement of the knee
Lateral compartment replacement of the knee
https://cardiffhipandknee.com/knee/partial-knee-replacements#sigProId489e7efa6a
3. Patellofemoral joint (Front of the knee)
About 5% people with knee arthritis have problems affecting predominantly the front of the knee (patellofemoral joint). In this situation, replacement of only the front of the knee joint is possible. This preserves the normal part of the knee, including the cruciate ligaments, and allows relatively normal kinematics.
X ray on the left is a side view showing loss of space between the patella (kneecap) and the femur (thigh bone). This has been treated with a replacement comprising a metal component fixed to the femur and a plastic (polyethylene) component cemented to the back of the knee cap.
In the carefully selected patient with isolated arthritis of the front of the knee, this operation gives excellent pain relief and function.
-
 patellofemoral arthritis of the knee
patellofemoral arthritis of the knee
patellofemoral arthritis of the knee
patellofemoral arthritis of the knee
-
 Patellofemoral replacement of the knee
Patellofemoral replacement of the knee
Patellofemoral replacement of the knee
Patellofemoral replacement of the knee
https://cardiffhipandknee.com/knee/partial-knee-replacements#sigProIdcaa7913a2b
Each of these joints can be resurfaced individually, as long as the other two parts of the knee joint are relatively intact and not causing any clinical symptoms.
"The operation has made it much easier to do normal walking and going up and down stairs. I am no longer limited by how my knee feels "- Cheryl Lloyd, Cardiff
ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE
Advantages of partial knee replacement (unicompartmental knee replacement)
1. The main advantage of doing partial knee replacements is that most of the knee joint surface, and all the ligaments are left intact, hence providing a more physiological function. Such physiological function is not always achievable after total knee replacement, despite tremendous improvements in technology for total knee replacements. A greater number of people feel their knee is 'normal' after partial knee replacement compared to total knee replacement patients.
2. The incision for surgery is generally smaller, and involves lesser trauma to the tissues compared to total knee replacements. The recovery is faster and there is less postoperative discomfort.
Disadvantages
1. Progression of arthritis in the remaining part of the knee joint can cause recurrence of pain, and this requires conversion to a total knee replacement.
2. The predictability of partial knee replacements to provide long term pain relief is not as good as total knee replacements. A small percentage need to be converted to total knee replacement for this reason.
3. Careful selection of patients is critical to achieve the best outcome and minimise suboptimal results.
The general risks of partial knee replacement surgery are largely similar to total knee replacement.
If you have further questions, please contact us about your query, and I will be delighted to respond to any comments, questions or concerns.
